The September 2024 edition of IALR at a Glance is jam-packed with exciting news and updates! Learn more about…
- IALR Supporting Industrial Fermentation
- CMA Achieves ISO Certification
- IALR Interns Make a Real Impact
- Much more!
The September 2024 edition of IALR at a Glance is jam-packed with exciting news and updates! Learn more about…

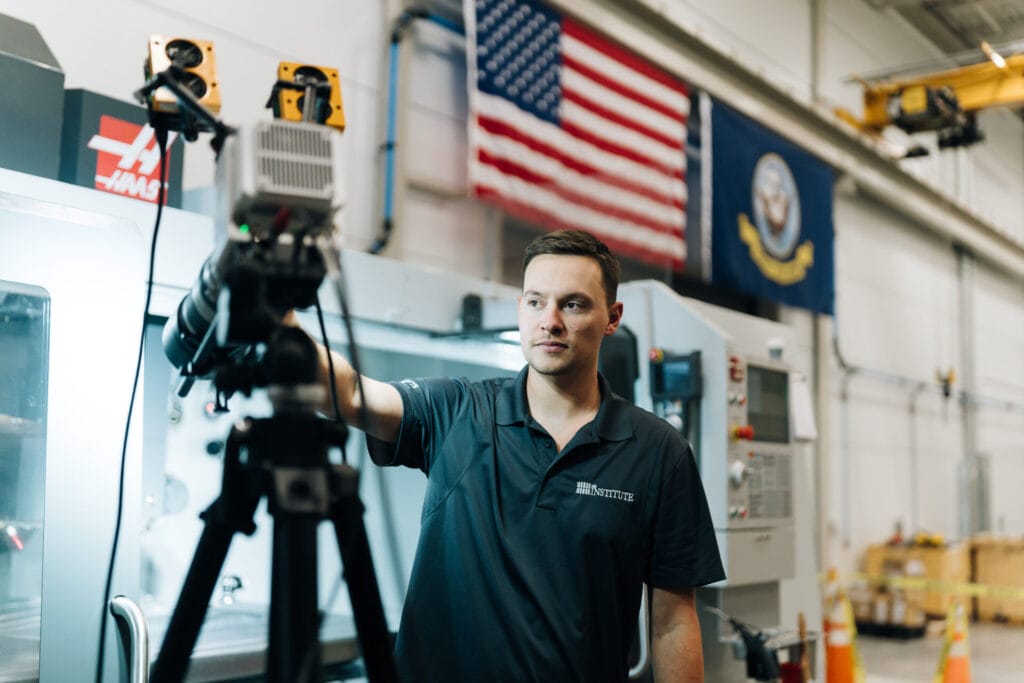
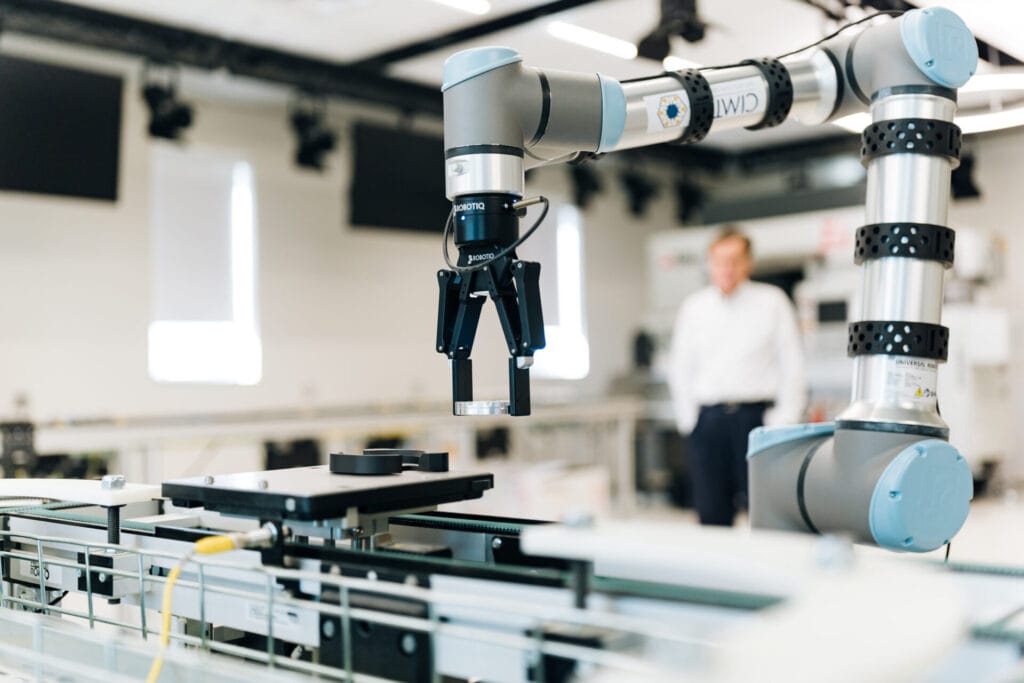
The “Inside IALR” team showcases the CNC Innovation Lab inside the Center for Manufacturing Advancement (CMA) with CMA Operations Manager Kevin Thompson and CNC Technologist Jeremiah Williams. This episode highlights how the 5,791-square-foot CNC Machining Innovation Lab enables new and existing businesses to evaluate their processes, build out improvements and incorporate efficiencies without disrupting current operations. This space empowers manufacturers to increase global competitiveness (02:44). They discuss the role of CNC machining (04:18) and its primary role within the manufacturing industry (06:06). The equipment and processes (08:27) are the main attraction for industry. Kevin and Jeremiah explain the specific services provided by the CNC Innovation Lab (14:46) and also provide a short explanation of the Navy’s Additive Manufacturing Center of Excellence (AM CoE) and how the CNC Lab fits into that (19:14).

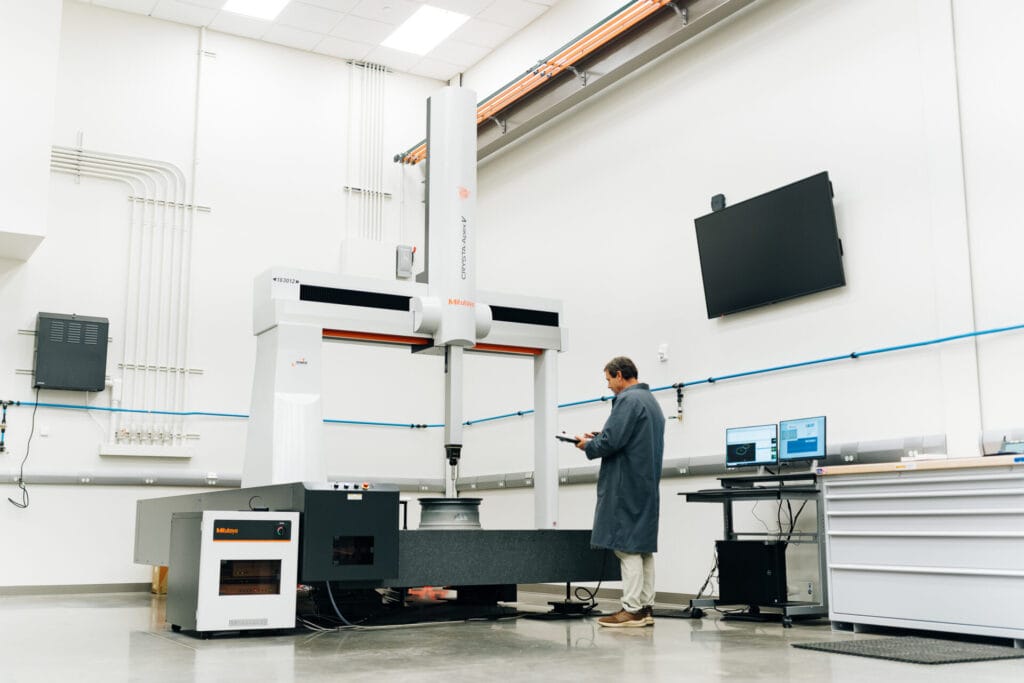
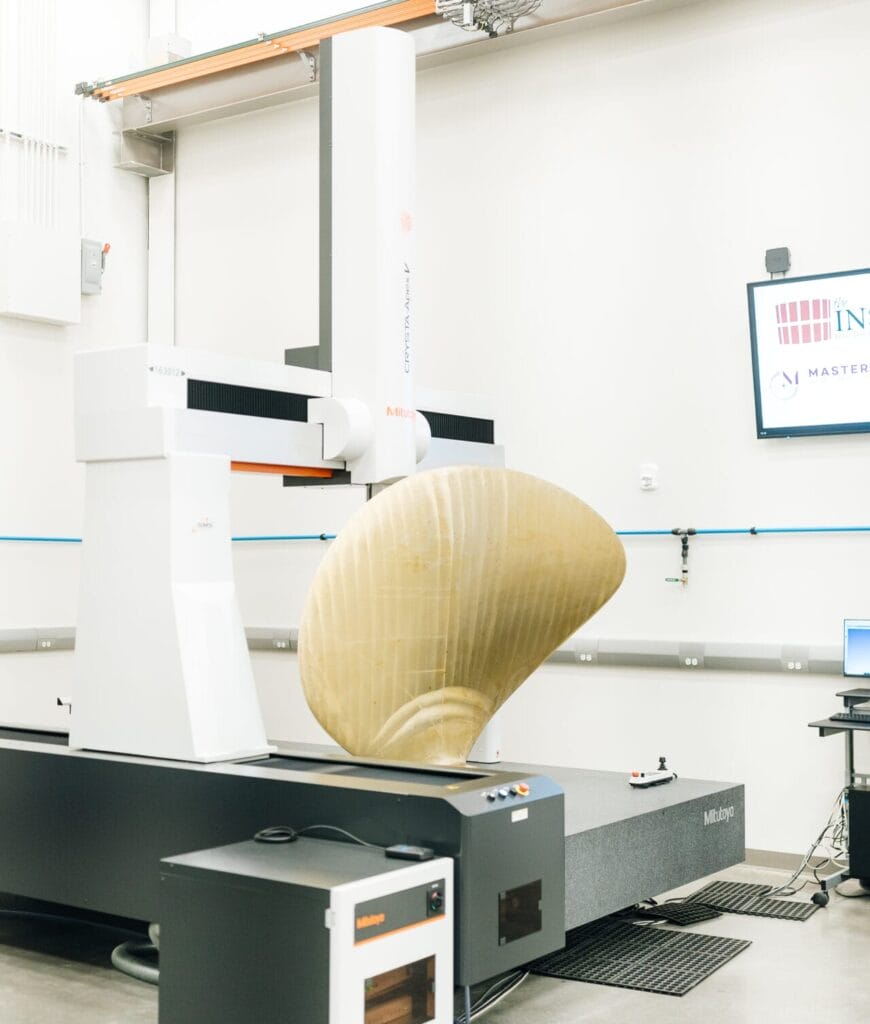
That’s how many points are scanned per second on the laser scanner on the Mitutoyo Crysta-Apex V163012 Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM), one of the largest on the East Coast. Even a relatively small part has tens of millions of scannable points. In addition to the laser scanner, the CMM boasts a variety of unique qualification and measurement capabilities.
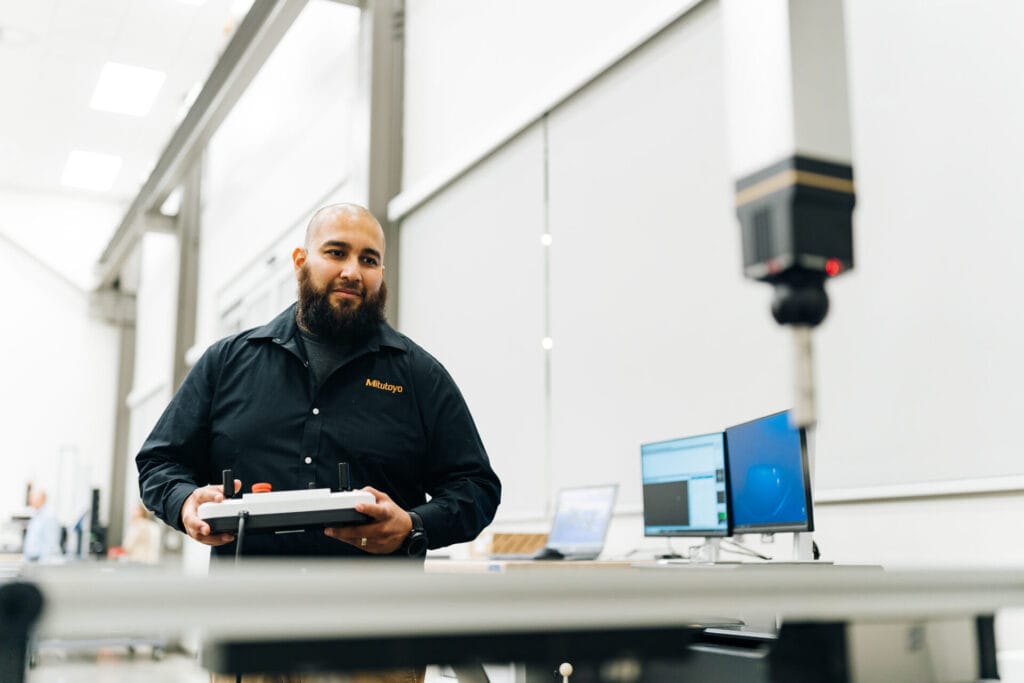
Equipped with the CMM and a bevy of other top-tier qualification tools and equipment, the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research’s (IALR) Metrology Lab provides critical measurement and qualifications services for the Navy’s Additive Manufacturing Center of Excellence (AM CoE) and has the capability to provide support for private industry. Located inside the Center for Manufacturing Advancement in Southern Virginia, the Metrology Lab with NIST Certified Inspection is the result of strong partnerships. IALR owns the equipment and space, but applications engineers with Mitutoyo and Master Gage & Tool Co. operate the equipment.

“The Metrology Lab is a unique resource for local industry and a key component of the Navy’s efforts to improve additive technologies and processes. The Metrology Lab also epitomizes several core tenets of IALR, including our mission of economic transformation, commitment to partnerships and penchant for utilizing state-of-the-art technology.” – Tim Robertson, Chief Operating Officer, Manufacturing Advancement
 Top-Tier Metrology Through Partnerships
Top-Tier Metrology Through PartnershipsMetrology, officially defined as the science of measurement, is a crucial element of any manufacturing process. In the Metrology Lab at IALR, application engineers can perform relatively simple measurements, such as physical dimensions, and highly complex qualifications of factors like shape, hardness and many other physical qualities.
The CMM inside the Metrology Lab can perform some of the most sophisticated yet critical measurement and qualification processes possible. It has a work area that can accommodate pieces as large as five feet wide, nearly 10 feet long and almost four feet tall, but the space can also be used for smaller parts. For instance, staff could place dozens of the same parts on the surface area and program the CMM to perform identical qualification tasks on each.
“The Mitutoyo Crysta-Apex V163012 Coordinate Measuring Machine can pretty much do any type of inspections that would be needed in the industry.” – Carlos Cabello, Applications Engineer, Mitutoyo
Every measurement the machine makes is down to the micron.
Some of the services offered by the Metrology Lab with NIST Certified Inspection include:

The Navy established its Additive Manufacturing Center of Excellence (AM CoE) inside the CMA. Tasked with scaling and maturing additive technologies for the production of submarine components to bolster naval shipbuilding and repair supply chains, the AM CoE includes the Navy and nine other organizations. The AM CoE team develops new technical data packages (TDP), which are essentially comprehensive “recipes” for utilizing additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, techniques to manufacture particular components.
The Metrology Lab – as well as the CNC Machining Innovation Lab that IALR owns and operates – plays a critical role in this operation. In fact, the team in the Metrology Lab will conduct three separate inspections of every part:
“It’s very honorable work, and I’m very proud to be a part of this project.” – Sean Cobb, Master Gage and Tool
While the AM CoE utilizes the lab to complete numerous inspections, the partners can also use the equipment to provide services and support to industry. The CMM and other equipment allows industry in need of testing support to accurately and affordably measure and certify products.
“In order for a company to do this level of measurement and qualification, they’re going to have to make major capital investments and slow down production. We can provide those testing services in a convenient and certified way without impeding production.” – Kevin Thompson, CMA Operations Manager
The Center for Manufacturing Advancement, which houses the Navy’s AM CoE and impactful technology and resources like the Metrology Lab, is located in Danville, Virginia, on the IALR campus. Companies that are interested in partnering with IALR in the CMA by utilizing the services of the Metrology Lab, collaborating with the CNC Innovation Lab, or learning about automation in the Industry 4.0 Integration Lab should contact the IALR team.


A specialized camera that shoots up to 400,000 frames per second, allowing true slow-motion views of the manufacturing process.
Cutting-edge sensors that measure factors like cutting force and harmonic vibrations.
Infrared cameras that show temperature patterns throughout an operation.
These are just a few of the specialized pieces of equipment within the Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining Innovation Lab, which is housed inside the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research’s (IALR) Center for Manufacturing Advancement (CMA). The CNC Machining Innovation Lab also plays a crucial role in the U.S. Navy’s Additive Manufacturing Center of Excellence (AM CoE), also housed within the CMA.
Featuring state-of-the-art equipment and cutting-edge technology, the CNC Machining Innovation Lab will support private industry through testing services and process optimization and help the AM CoE develop world-leading additive manufacturing “recipes” for the development of parts needed by the U.S. military.

“The vision of the CNC Machining Innovation Lab is twofold. We support the AM CoE, but we also have a vision to support industry. We’re trying to develop partnerships to help industry drive innovation and productivity with increased profitability in a rapidly changing environment.” — Kevin Thompson, Operations Manager for the Center for Manufacturing Advancement, IALR
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining is a manufacturing process where computer-controlled machines create precise and intricate parts and components. Commonplace in industries such as aerospace, electronics and healthcare, this is a subtractive manufacturing process – meaning that an existing block or item is whittled down or shaped.
The CNC Machining Innovation Lab partners with public and private manufacturers of all sizes to modernize their processes, identify and integrate emerging technologies and provide data-driven process development and optimization. Some of the capabilities include process development, process optimization, CNC programming, the integration of emerging technology, automation integration, turn-key solutions and application engineering support.
“Companies don’t have the capacity to be able to stop and try a new process. They have to find external ways of doing that, and that’s a huge role we can play. Companies can present a challenge to us and continue to produce goods while we develop a solution that suits their needs.” — Jeremiah Williams, CNC Technologist, IALR

The CNC Machining Innovation Lab boasts a broad inventory of specialized equipment, including sensors to measure factors like cutting force, slow-motion cameras to track chip formation, infrared cameras to analyze the impact of heat and much more, all with the goal of “trying to optimize processes for customers,” Thompson explains. IALR is even allowing other companies to test and utilize specialized sensors inside of the CNC Lab machines for data collection.
“Our job is not to compete with industry. Our job is to support industry.” – Kevin Thompson, Operations Manager for the Center for Manufacturing Advancement, IALR
Businesses can:
The CNC Machining Innovation Lab is ISO 9001:2015 compliant, reassuring customers and partners alike that we have an internationally validated system in place to address and prevent quality issues.
The CNC Machining Innovation Lab is located across from the CMA’s state-of-the-art Metrology Lab that features one of the largest Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) on the East Coast with 3D scanning capability along with optical measurement systems, hardness and roundness testers and support equipment. Through a partnership with Mitutoyo and Master Gage & Tool, IALR offers the services of the Metrology Lab to regional businesses and partners who may not otherwise have access to such capabilities.
“The Metrology Lab is ideal for emerging or developing businesses to have access to this capability while building justification for their own capital investment.” – Kevin Thompson, Operations Manager for the Center for Manufacturing Advancement, IALR
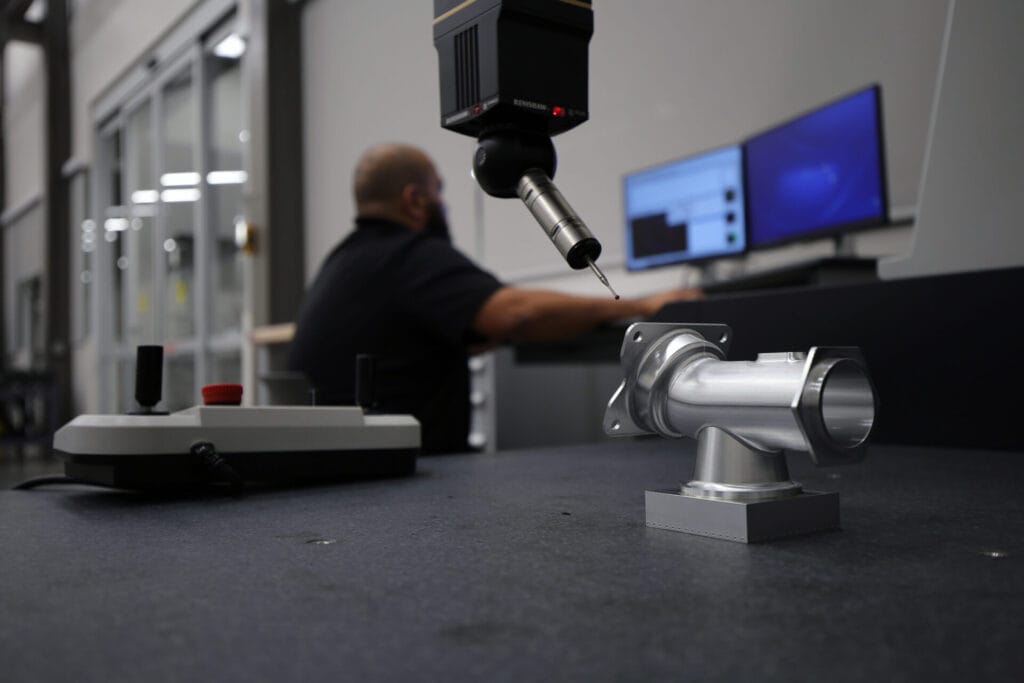

“Everything we do at IALR involves partnerships and is driven by the needs of industry. Through the CNC Machining Innovation Lab and the Metrology Lab, IALR is simultaneously contributing to our nation’s defense and supporting current, new and prospective companies in Southern Virginia with needed services.” – Telly Tucker, IALR President
The CMA also includes a dynamic Industry 4.0 Integration Lab that serves as a demonstration site, showing manufacturing companies what is possible. Companies that are interested in partnering with IALR in the CNC Machining Innovation Lab or in the CMA should contact the IALR team.

The submarine industrial base (SIB) is a system of thousands of companies that produce parts and equipment used in the production and maintenance of submarines for the U.S. Navy. IALR has partnered with the U.S. Navy – along with many other public and private organizations – in a two-pronged approach to support the SIB, the development of new submarines, and the maintenance of the existing fleet: the federal Accelerated Training in Defense Manufacturing (ATDM) program and the U.S. Navy’s Additive Manufacturing Center of Excellence (AM CoE).
ATDM increases the pool of skilled labor in areas like additive manufacturing, CNC machining, welding, metrology and non-destructive testing – trades that are needed by the SIB. On the other hand, the AM CoE is focused on implementing additive technologies and processes that will allow for more efficient development of parts. Don Hairston, General Manager of Austal USA Advanced Technologies, used the analogy of making cookies during a recent presentation at the ATDM AM CoE Summit at IALR. When making cookies and especially in manufacturing parts for the U.S. Navy, each of these variables must be accounted for and done correctly for successful production: raw materials, equipment, manufacturing know-how, post-processing and finishing and quality control.
In the simplest terms, “scaling the supply chain” is one of the primary goals of the AM CoE, Hairston explained.
The AM CoE will scale and mature additive technologies that enable innovative production of submarine components to bolster naval shipbuilding and repair supply chains. Involving nine different partners, the AM CoE will increase overall manufacturing capacity and close the supply-demand gap in critical markets like castings, forgings, fittings and fasteners.
The AM CoE team will develop new technical data packages (TDP), which are essentially comprehensive “recipes” for how to utilize additive manufacturing techniques to manufacture particular components. The workflow inside the AM CoE will typically go something like this:
As part of the Navy’s AM CoE, the CNC Machining Innovation Lab will be utilized after the initial printing of a part, verifying that the design used for additive manufacturing can successfully be machined. Simultaneously, the IALR team will also explore and implement advanced strategies that better align with today’s manufacturing equipment and methods.
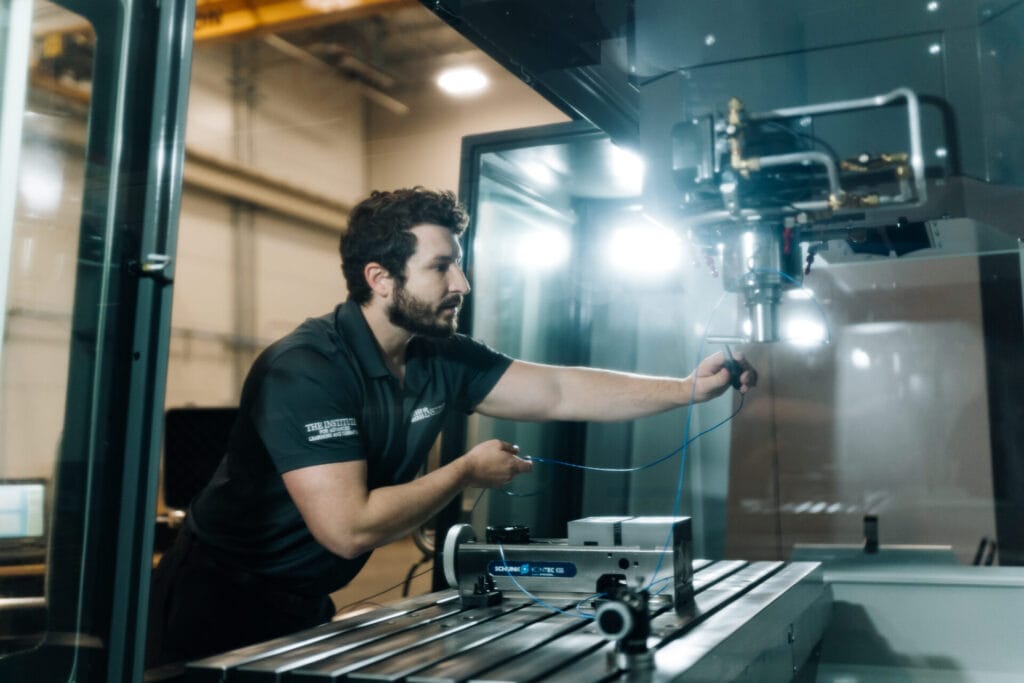

“Basically, what we will do is verify that the part that has been printed can be successfully and correctly machined without any issues.” – Jeremiah Williams, CNC Technologist
Additive manufacturing, which can also be referred to as 3D printing, is a subset of manufacturing where an object is built “from the ground up” based on a 3D model. It may seem odd that a subtractive manufacturing method would play such an integral role in the Navy’s additive manufacturing operations. While 3D printing and additive manufacturing are the primary focus of the AM CoE, subtractive methods are still essential in creating and verifying any part.
“With the current technology and dimensional requirements of the parts, you can’t simply print and install a component. You’re going to have to print it and then do some final subtractive work before the part can be utilized.” – Jeremiah Williams, CNC Technologist
Once perfected and tested, the TDPs will be shared with Navy suppliers, providing them with the “recipe” they need to produce the part correctly and efficiently. As of mid-October, the AM CoE has released 28 TDPs to the companies that will be manufacturing the parts.